How to Check Database Size in Linux
Introduction
MySQL provides valuable metadata about databases and tables. For example, if a database's system memory runs out, checking the database or table size helps identify where the storage is particularly overwhelmed.
This article provides three methods to check the size for all MySQL databases, a single database, or a table within a database.
Prerequisites
- A MySQL database with populated tables.
- Access to the command line/terminal.
- phpMyAdmin or MySQL workbench installed and configured (optional).
Note: For storage-heavy workloads and overwhelmed databases, we recommend you deploy a memory-optimized Bare Metal Cloud server. The server instance comes with up to 768GB of RAM and scalable processors to ensure stability during peak times.
How to Check MySQL Database and Table Size
There are three ways to check MySQL database and table sizes:
1. Using phpMyAdmin.
2. Using the SELECT statement.
3. Using MySQL workbench.
All methods provide ways to check the size for:
- A single database.
- All databases.
- Table size for a single database.
- Table size for all databases.
Choose a method that best fits your configuration and follow the step-by-step instructions below.
Method 1: Using phpMyAdmin
Use the phpMyAdmin web interface to access information about MySQL databases and tables, including their sizes. Start by logging into your phpMyAdmin administration page.
Get the Size for a Single Database
Follow these steps to check the size for a single database using phpMyAdmin:
1. Select the database name on the left pane.
2. Locate the Size column. The individual table sizes display in the output.
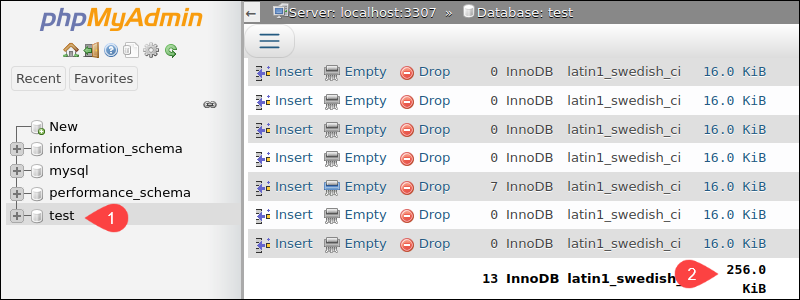
Scroll to the bottom to see the total size for the selected database, which is the total sum.
Get the Size for all Databases
To find the size of all databases in phpMyAdmin:
1. On the index page, locate and select the Databases tab in the top navbar.
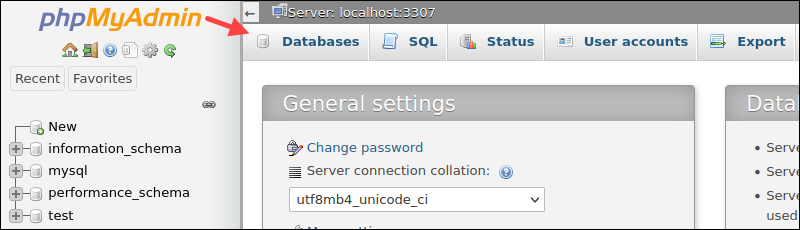
2. Below the table, select Enable statistics.
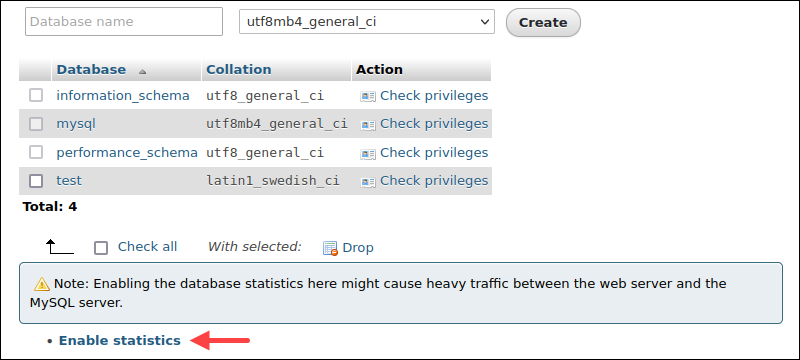
Enabling statistics can cause high traffic between MySQL and web servers. Use this method when there's low traffic to minimize server overload.
3. The Database statistics page displays general statistics about all the databases, including the size. The column Total sums the Data and Indexes columns.
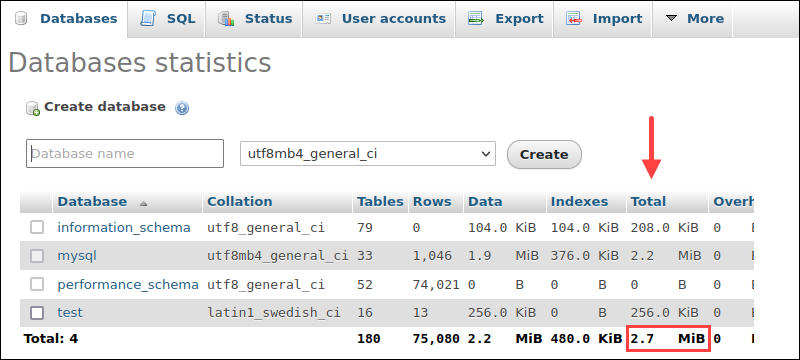
The last row shows the sizes summed up.
Get Table Size for a Single Database
To check the size for a single database table:
1. Click a database name in the left pane to select a database.
2. Use the search bar to filter tables by name.
Alternatively, locate the table manually in the list below the search bar.
3. Find the Size column and check the table size.
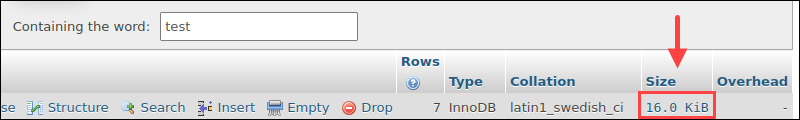
If not immediately visible, scroll the table to the right until the column is visible.
Get Table Size for All Databases
Check all database table sizes in phpMyAdmin using the SELECT query.
1. On the index page, select the SQL tab.
2. Enter the following query to display the table size for all databases:
SELECT TABLE_SCHEMA AS `Database`, TABLE_NAME AS `Table`, ROUND((DATA_LENGTH + INDEX_LENGTH) / 1024 / 1024) AS `Size (MB)` FROM information_schema.TABLES ORDER BY (DATA_LENGTH + INDEX_LENGTH) DESC; 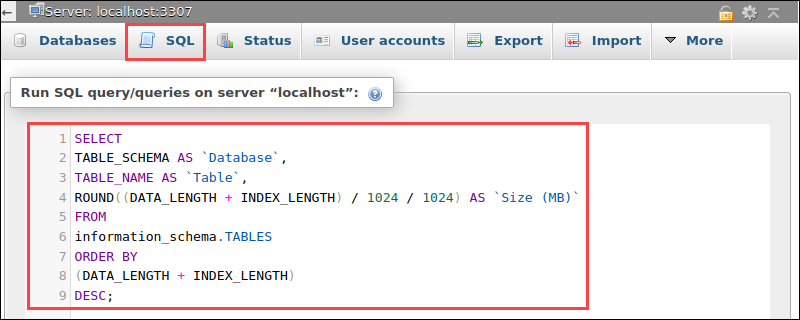
Divide twice by 1024 to get the size in MB and once in KB. Press Go to run the query and fetch the result.
3. The output shows the table sizes for all databases in the last column.
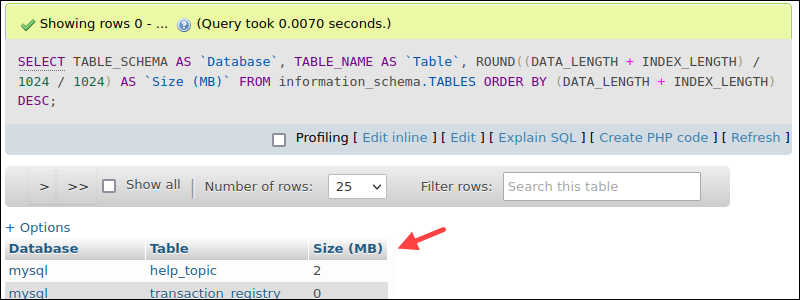
4. Drag and drop the columns to manage the order, or click on the column name to sort the output.
Method 2: Using the SELECT MySQL Command-Line Statement
The database and tables sizes are available through the MySQL command-line interface.
1. Open the terminal (CTRL+ALT+T) and start the MySQL monitor with:
mysql -u <username> -p 2. Type the password when prompted and press Enter. The terminal shows the mysql> prompt.
Below are several example queries using the SELECT statement. All the outputs show the size in MB with two decimal places.
Get the Size for a Single Database
Use the SELECT statement to get the size of a single database:
SELECT TABLE_SCHEMA AS `Database`, ROUND(SUM(DATA_LENGTH + INDEX_LENGTH) / 1024 / 1024, 2) AS `Size (MB)` FROM information_schema.TABLES WHERE TABLE_SCHEMA="<database name>"; 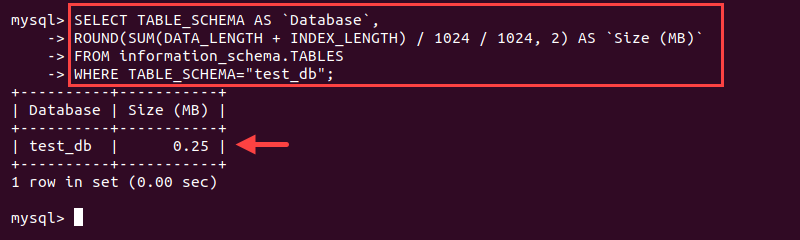
Change the <database name> to the database you'd like to check.
Get the Size for all Databases
View the size of all databases with the following query:
SELECT TABLE_SCHEMA AS `Database`, ROUND(SUM(DATA_LENGTH + INDEX_LENGTH) / 1024 / 1024, 2) AS `Size (MB)` FROM information_schema.TABLES GROUP BY TABLE_SCHEMA ORDER BY SUM(DATA_LENGTH + INDEX_LENGTH) DESC; 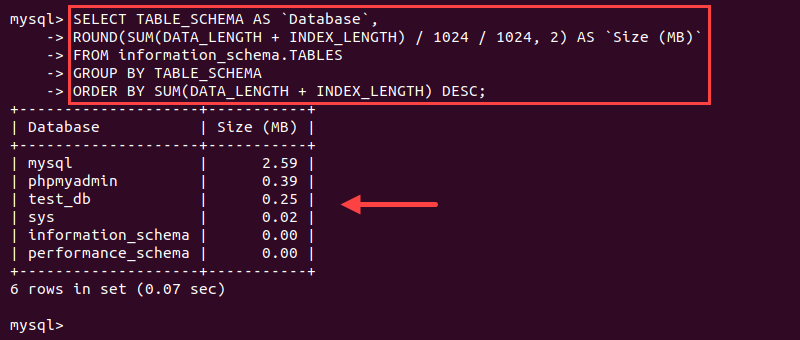
The output shows database sizes sorted in descending order in MB.
Get Table Size for a Single Database
List table sizes for a single database by using:
SELECT TABLE_NAME AS `Table`, ROUND(((DATA_LENGTH + INDEX_LENGTH) / 1024 / 1024), 2) AS `Size (MB)` FROM information_schema.TABLES WHERE table_schema = "<database name>" ORDER BY (data_length + index_length) DESC; 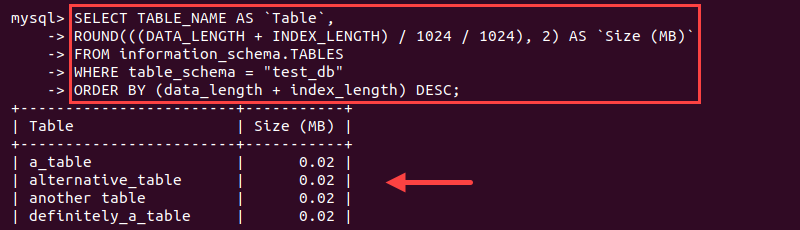
Exchange <database name> for the actual database name. The output sorts the tables by size in descending order in MB.
Get Table Size for All Databases
Show table sizes for all databases with:
SELECT TABLE_SCHEMA AS `Database`, TABLE_NAME AS `Table`, ROUND((DATA_LENGTH + INDEX_LENGTH) / 1024 / 1024) AS `Size (MB)` FROM information_schema.TABLES ORDER BY (DATA_LENGTH + INDEX_LENGTH) DESC; 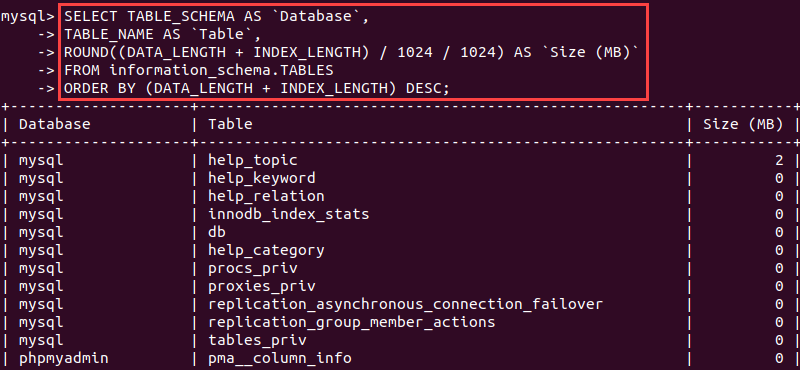
The query sorts the output by database size. Change the last line to sort by a different parameter.
Method 3: Using MySQL Workbench
The SELECT query methods work equally well for MySQL Workbench. However, the program provides two additional ways to quickly check the size of a single database and the tables inside a database.
Start by opening MySQL Workbench and establish a connection.
Get the Size for a Single Database
1. To get the size of a single database in MySQL Workbench, right-click on the schema you want to check in the left navigation pane.
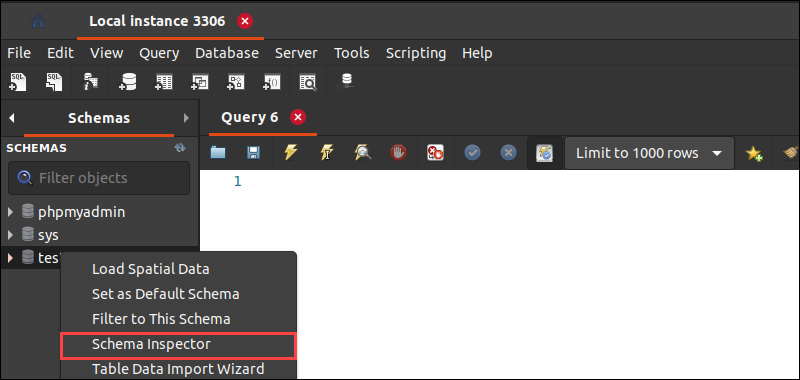
2. Select Schema Inspector from the list. On the right pane, under the Index tab, check the database size.
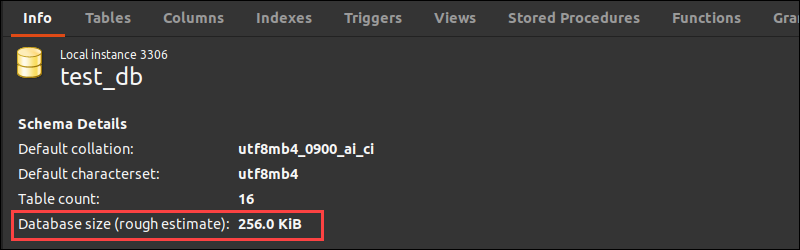
The size is a rough estimate displayed in binary bytes.
Get Table Size for a Single Database
To get the size of a table of a specific database:
1. Open the Schema Inspector for the database where the table(s) reside.
2. Navigate to the Tables tab.
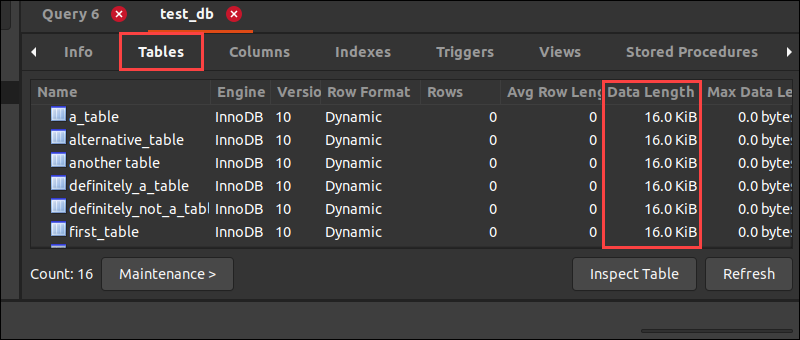
3. Check the size of a specific table in the Data Length column or add them together to get the total amount. Alternatively, use the SELECT statement in a query.
Table Size Limits
MyISAM tables have a default limit set to 256TB for data and index files, which you can change to 65,536TB maximum.
InnoDB maximum size for tables is 256TB, which corresponds to the full tablespace size. Generally, the best practice is to divide an InnoDB table into multiple tablespaces.
Depending on the specifications, some operating systems limit the file size. Although MySQL has some table size limits, a full table error is most likely due to the operating system. Alternatively, the storage where the database resides is possibly at full capacity.
Conclusion
You should now know several methods to get database and table sizes after following this tutorial. Next, read how to optimize MySQL tables and other get other MySQL Performance Tuning and Optimization Tips.
Was this article helpful?
Yes No
How to Check Database Size in Linux
Source: https://phoenixnap.com/kb/mysql-database-size